AI & Sewer Defect Analysis
Competition: Innovation in Water Challenge
Amount awarded: £189,315
Led by: United Utilities
Partners: Dŵr Cymru (Welsh Water), Scottish Water, Severn Trent Water, Thames Water, Water Research Centre, and Yorkshire Water Services
Project completed: October 2023
Water cycle tag: Waste water network
Water companies and their supply chain are using Artificial Intelligence (AI) models to review wastewater pipe CCTV footage to spot defects and assess pipe condition. These AI models offer higher productivity compared with conventional human-centric approaches, but take-up is limited. Like all IT systems, they rely on high quality data which is not widely available. This project offers a dataset of cleaned and categorised images for third parties to update their AI models and offer new services.
This project aimed to align with the Ofwat Innovation theme to deliver long-term operational resilience and understanding infrastructure risks to customers and the environment, finding solutions to mitigate these in sustainable and efficient ways.
Sector-wide problem
- Water companies rely on a network of wastewater pipes to provide their services to customers.
- These sewers are critical infrastructure; maintenance is of high importance and their condition must be understood.
- It is estimated that collectively over £20 million is spent annually inspecting these pipes. CCTV inspection of sewers provides a method for asset condition assessments.
- To enable repairs and replacement to be completed efficiently, the defects and features of sewers are classified by engineers using the CCTV footage.
- The process is slow, labour intensive and repetitive. The accuracy of the classification is important but can be difficult to achieve. In parallel, AI is widely used for object / facial recognition in many sectors.
- AI can be used to improve the accuracy of the classification and reduce the overall time required. However, AI models must be trained before they can perform object recognition, which requires accurate data.
- Obtaining this data for AI development and use is a significant obstacle for adoption of this technology – potential productivity gains are therefore limited. We need more data available to more AI providers.
Project objective
- Provide a single benchmark data set against which to reference the images captured for coding
- To make this dataset freely available any third party
Project implementation
Coded CCTV survey footage from several UK water companies was provided to WRc who collated the footage into a central storage location. In total, over 725,000 images were collated and analysed.
Following feedback from AI providers and water companies, a common standard format for the coded CCTV survey footage was specified.
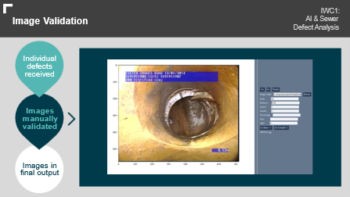
The defect images and metadata were manually validated to ensure the images and metadata were suitable for AI model training. For each defect, one image was selected that was most suitable for training an AI model. For the images to be suitable for training an AI model they needed to:
- Contain a defect
- Be of straight down the pipe with the pipe centred in the frame
- Have the pipe and defect not obscured by anything such as text
Where multiple images of a defect (as 5 images per defect had been taken forward from the image selection stage) met the above requirements, the clearest image was selected.
Limitations
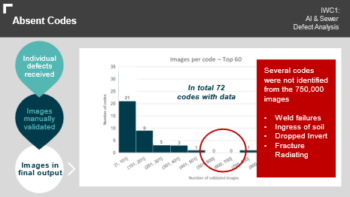
The project focussed on most common defect types for most impact; therefore, some defect codes and types could not be gathered due to low volume of data or unvalidated images.
Outcomes, impact and future potential
- Outcomes: All project objectives were achieved. Over 27,000 images are now available in the freely available dataset including images and data describing defects that are new to AI providers
- Impact: This was the first time cross-sector sharing of CCTV footage to cover wide variety of conditions, materials and methods – a global first of cloud-based data set of images for the use of image coders and AI software vendors. Many AI providers have updated their AI models – with water companies and their supply chain benefitting from this improved model
- Future potential: We encourage more AI providers to use this free dataset update their models – this reduces the adoption cost of AI and should lead to more water companies adopting AI – at least 4 water companies are now using the dataset via their external AI provider. The sector could consider further investment over time to maintain and increase the dataset.